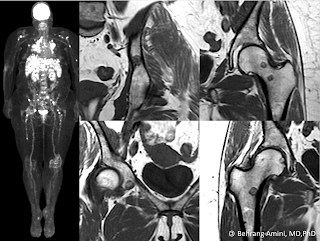
FDG PET and MRI of a patient with sarcoidosis and fat-containing bone lesions.
The presence of fat within a bone lesion is almost always reassuring, although rare exceptions exist. The following differential diagnosis is based on a combination of published papers and my own anecdotal experience:
- Hemangioma:
- Intra-osseous lipoma and lipoma variants, including fibrolipoma, angiolipoma and myelolipoma.
- Enchondroma:
- Liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor (LSMFT): Nearly all occur in the intertrochanteric region. Now felt to represent a variant of fibrous dysplasia.
- Osteoporosis: Can give the appearance of lucent bone lesions on CT. These won't have defined margins, and measurement of internal attenuation will reveal the fatty nature of the lesion.
- Bone infarction: Trivial, but included for the sake of completeness
- Paget disease of bone:
- Focal red marrow rest: Ill-defined, intermediate T1 signal. May contain subtle areas of internal fat.
- Lymphoma: Not truly a fat-containing lesion, but can entrap fat as the tumor infiltrates marrow.
- Sarcoid: The case above shows a patient with sarcoid and nodal, hepatic, and osseous involvement. Can have fuzzy margins ("brush border").
- Treated metastasis: One of the ways metastases respond to therapy is by developing internal fat. Myeloma lesions can even entirely "disappear" due to fatty replacement.
- Indolent metastases: Medullary thyroid cancer, adenoid cystic carcinoma.
- Intra-osseous hibernoma: Rare.
- Solid variant of aneurysmal bone cyst:
- Nonossifying fibroma:
- Erdheim-Chester disease:
- Malignancy arising from a fat-containing lesion: For example, osteosarcoma arising from bone infarction or Paget.
References
- Kumar R, Deaver MT, Czerniak BA, Madewell JE. Intraosseous hibernoma. Skeletal Radiol. 2011 May;40(5):641-5.
- Moore SL, Kransdorf MJ, Schweitzer ME, Murphey MD, Babb JS. Can sarcoidosis and metastatic bone lesions be reliably differentiated on routine MRI? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012 Jun;198(6):1387-93.
- Simpfendorfer CS1, Ilaslan H, Davies AM, James SL, Obuchowski NA, Sundaram M. Does the presence of focal normal marrow fat signal within a tumor on MRI exclude malignancy? An analysis of 184 histologically proven tumors of the pelvic and appendicular skeleton. Skeletal Radiol. 2008 Sep;37(9):797-804.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.