- Type I: Normal configuration.
- Type II: Replaced or accessory left hepatic artery arising from the left gastric artery.
- Type III: Replaced or accessory right hepatic artery arising from the superior mesenteric artery.
- Type IV: Combination of replaced types II and III (double-replaced pattern).
- Type V: Common hepatic artery arising from the superior mesenteric artery.
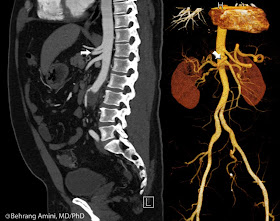
- Type VI: Common hepatic artery arising from the aorta (case shown here, arrows).
This classification is not all-inclusive, and many other variants can exist.
A replaced hepatic artery is the sole such arterial trunk. For example a person with a replaced right hepatic artery will not have another right hepatic arterial supply arising from the celiac axis. An accessory hepatic artery, on the other hand, will be just what its name suggests: an extra arterial supply. For example a patient with an accessory right hepatic artery will also have a normal right hepatic arterial supply.
References
Hiatt JR, Gabbay J, Busuttil RW. Surgical anatomy of the hepatic arteries in 1000 cases. Ann Surg. 1994 Jul;220(1):50-2.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.